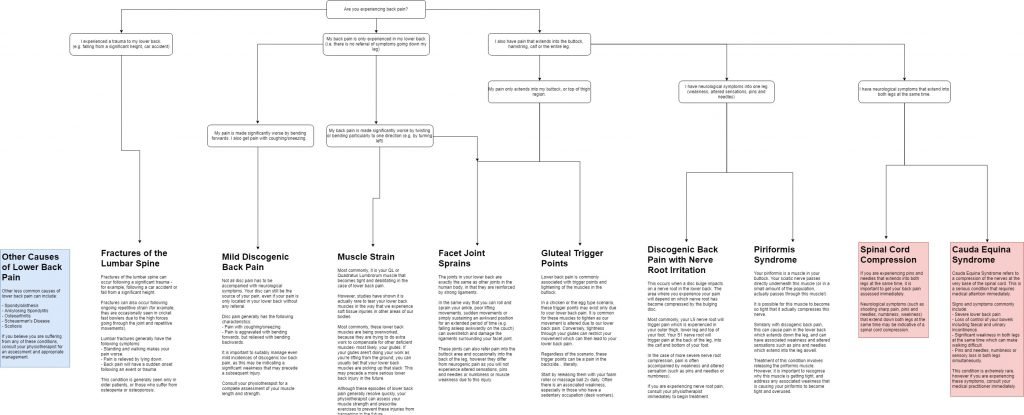
Diagnose Your Own Back Pain | Move Physiotherapy East Fremantle
The following flowchart is a guide for self-diagnosing your short-term lower back pain.
Based on the mechanism and history behind your back pain, it aims to provide you with an insight into your potential diagnosis.
Due to the complexity in treating back pain, and the specific exercise rehabilitation required to remove this pain and ensure you remain pain-free in the future, it is important to consult your physiotherapist as early as possible. Move Physiotherapy are experts in general physiotherapy and sports physiotherapy, and, regardless of whether you are simply aiming to return to daily life pain free, or get back to your favourite sport or activity, we can get you back to the activities you love in the quickest time frame. You can follow the link at the top of the page to book online.

Please also note, this is by no means an exhaustive list of pathologies that cause back pain. It is important that if you are experiencing neurological symptoms that are extending into both legs (e.g. pins and needles, numbness, weakness) that you consult a physiotherapist or medical practitioner immediately as this may be a sign of a more sinister pathology.
If you are experiencing recurrent pain it is important to get this assessed by your physiotherapist. Minor incidents of pain should be treated as a warning sign of a potentially more significant event.
This flowchart is a guide on the most common causes of short term lower back pain, such as discogenic pain, facet joint sprains and muscle strains. It also outlines common causes of sciatica including nerve root irritations and piriformis syndrome.
Also bear in mind, that if you are dealing with chronic/long term lower back pain, we need to shift our focus towards ‘why’ structures in your back are becoming overloaded/tight/painful. With more chronic conditions, our treatment will be aimed towards appropriate exercise rehabilitation to strengthen muscles (e.g. core or glutes) which will reduce the strain being placed onto your lower back.
Click on the image below to expand the image and view online.